Cytopathology
Cytopathology
1. Examining shed cells:
- Our bodies naturally shed cells in fluids like urine, lung fluid, or cerebrospinal fluid.
- Cytopathologists study these cells under a microscope to see if they are healthy or abnormal.
- If abnormal cells are found, it might indicate the presence of a serious condition like cancer.
2. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA):
- This is a minimally invasive procedure where a thin needle is used to collect a small sample of cells from a lump or suspicious area.
- The collected cells are then examined under a microscope for abnormalities.
3. Exfoliative cytology:
- This involves studying cells that naturally shed from the surface of tissues, such as:
- Cervical cancer screening: This is commonly known as a Pap smear.
- Vaginal smears: Used to check for infections or abnormal cell changes.
- Oral cytology: Helps detect precancerous and cancerous changes in the mouth.
4. Fluid cytology:
- This involves examining cells present in various body fluids, like pleural fluid (around the lungs) or peritoneal fluid (around the abdomen).
- This helps us check for the presence of malignant (cancerous) cells.
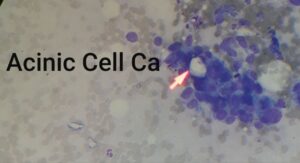
FNAC
Fine Needle Aspiration of Salivary Gland
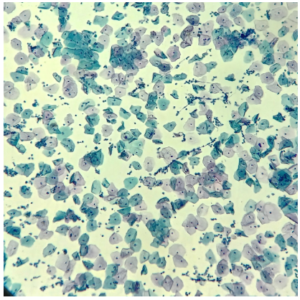
LBC -PAP Smear
Liquid Base Cytology -PAP smear
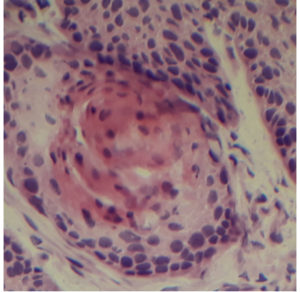
Ascitic Fluid
Malignant lesion in plural fluid


